Roofing Terminology and Parts
The first step to knowing your way around your roof is to understand what’s what.
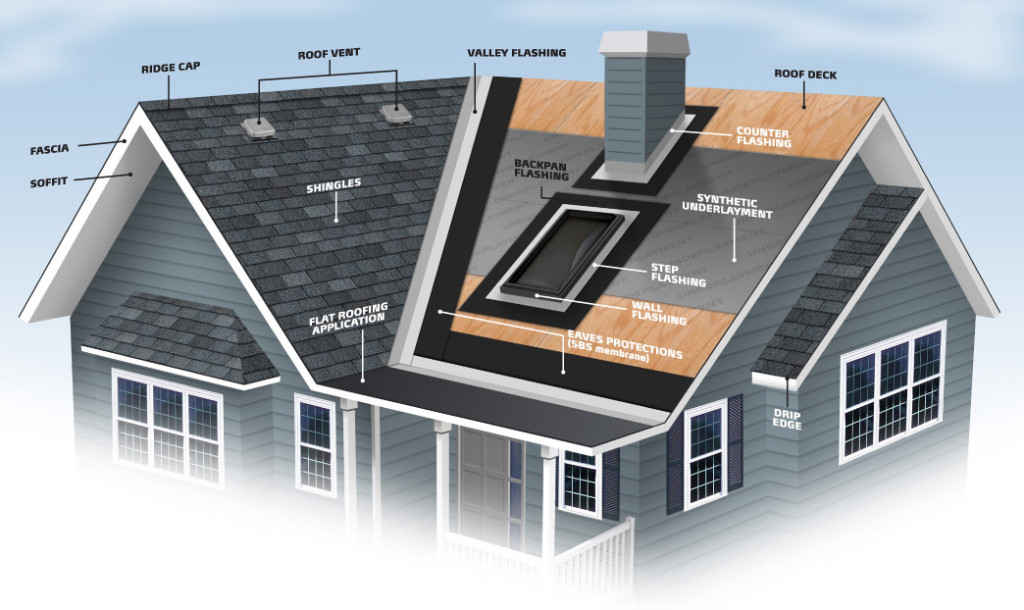
- Decking
- Sometimes called sheathing, usually plywood that covers the top of your roof rafters. Usually felt paper is applied over the decking and then the roofing over the felt paper.
- Felt Paper
- Paper made out of a tar-based material installed between roofing and the decking. Usually used on pitched roofs, 15# or 30#. Is usually applied in two layers on lower pitched roofs.
- Roofing
- Material used to water-proof the decking.
- Flashing
- Material used to waterproof any penetrations through the roofing, or used when a vertical wall butts up against the roofing.
- Roof Jack
- Another form of flashing, pre-made and designed to “flash” pipes that stick out of the roof.
More Detailed Roofing Definitions from Owens Corning
- Asphalt
- A bituminous waterproofing agent applied to roofing materials during manufacturing.
- Asphalt plastic roofing cement
- An asphalt-based cement used to bond roofing materials. Also known as flashing cement or mastic; should conform to ASTM D-4586.
- Base flashing
- That portion of the flashing attached to or resting on the deck to direct the flow of water onto the roof covering.
- Built-up roof
- A flat or low-sloped roof consisting of multiple layers of asphalt and ply sheets.
- Caulk
- To fill a joint with mastic or asphalt cement to prevent leaks.
- Collar
- Pre-formed flange placed over a vent pipe to seal the roof around the vent pipe opening. Also called a vent sleeve.
- Concealed nail method
- Application of roll roofing in which all nails are driven into the underlying course of roofing and covered by a cemented, overlapping course. Nails are not exposed to the weather.
- Condensation
- The change of water from vapor to liquid when warm, moisture-laden air comes in contact with a cold surface.
- Counter flashing
- That portion of the flashing attached to a vertical surface to prevent water from migrating behind the base flashing.
- Course
- A row of shingles or roll roofing running the length of the roof.
- Cricket
- A peaked saddle construction at the back of a chimney to prevent accumulation of snow and ice and to deflect water around the chimney.
- Deck
- The surface installed over the supporting framing members to which the roofing is applied.
- Dormer
- A framed window unit projecting through the sloping plane of a roof.
- Downspout
- A pipe for draining water from roof gutters. Also called a leader.
- Drip edge
- A non-corrosive, non-staining material used along the eaves and rakes to allow water run-off to drip clear of underlying construction.
- Eaves
- The horizontal, lower edge of a sloped roof.
- Eaves flashing
- Additional layer of roofing material applied at the eaves to help prevent damage from water back-up.
- Felt
- Fibrous material saturated with asphalt and used as an underlayment or sheathing paper.
- Flashing
- Pieces of metal or roll roofing used to prevent seepage of water into a building around any intersection or projection in a roof such as vent pipes, chimneys, adjoining walls, dormers and valleys. Galvanized metal flashing should be minimum 26-gauge.
- Gable roof
- A type of roof containing sloping planes of the same pitch on each side of the ridge. Contains a gable at each end.
- Granules
- Ceramic-coated colored crushed rock that is applied to the exposed surface of asphalt roofing.
- Gutter
- The trough that channels water from the eaves to the downspouts.
- Hip
- The inclined external angle formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes. Runs from the ridge to the eaves.
- Ice dam
- Condition formed at the lower roof edge by the thawing and re-freezing of melted snow on the overhang. Can force water up and under shingles, causing leaks.
- Low slope application
- Method of installing asphalt shingles on roof slopes between two and four inches per foot.
- Mansard roof
- A type of roof containing two sloping planes of different pitch on each of four sides. The lower plane has a much steeper pitch than the upper, often approaching vertical. Contains no gables.
- Normal slope application
- Method of installing asphalt shingles on roof slopes between 4 inches and 21 inches per foot.
- Organic felt
- An asphalt roofing base material manufactured from cellulose fibers.
- Pitch
- The degree of roof incline expressed as the ratio of the rise, in feet, to the span, in feet.
- Plastic Cement
- A compound used to seal flashings and in some cases to seal down shingles as well as for other small waterproofing jobs. Where plastic cement is required for sealing down shingles, use a dab about the size of a quarter unless otherwise specified.
- Rafter
- The supporting framing member immediately beneath the deck, sloping from the ridge to the wall plate.
- Rake
- The inclined edge of a sloped roof over a wall from the eave to the ridge.
- Ridge
- The uppermost, horizontal external angle formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes.
- Rise
- The vertical distance from the eaves line to the ridge.
- Roll roofing
- Asphalt roofing products manufactured in roll form.
- Run
- The horizontal distance from the eaves to a point directly under the ridge. One half the span.
- Saturated felt
- An asphalt-impregnated felt used as an underlayment between the deck and the roofing material.
- Sheathing
- Exterior grade boards used as a roof deck material.
- Shed roof
- A roof containing only one sloping plane. Has no hips, ridges, valleys or gables.
- Slope
- The degree of roof incline expressed as the ratio of the rise, in inches, to the run, in feet.
- Soffit
- The finished underside of the eaves.
- Square
- A unit of roof measure covering 100 square feet.
- Steep slope application
- Method of installing asphalt shingles on roof slopes greater than 21 in. per foot.
- Step flashing
- Flashing application method used where a vertical surface meets a sloping roof plane.
- Three-tab shingle
- The most popular type of asphalt shingle usually 12″ x 36″ in size with three tabs.
- Underlayment
- A layer of asphalt saturated (sometimes referred to as tar paper) which is laid down on a bare deck before shingles are installed to provide additional protection for the deck.
- Valley
- The internal angle formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes to provide water runoff.
- Vent
- Any outlet for air that protrudes through the roof deck such as a pipe or stack. Any device installed on the roof, gable or soffit for the purpose of ventilating the underside of the roof deck.






